This is part of a series of articles to show you solutions to common finance tasks related to financial planning, accounting, tax calculations, and auditing problems all implemented with the low-code KNIME Analytics Platform.
Gross Profit Margin (GPM) is a comprehensive financial indicator to monitor the business's financial health. It provides key insights into the company's profitability, mainly, in terms of how well the production costs are being managed. Revenue on the other hand gives a broad view of a company’s overall sales performance, it is not a sufficient measure for financial performance since it does not take into account the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS).
In this article, we will:
- Provide background information on the role of a financial analyst at "ABC Furniture" and an overview of the dataset we will use.
- Define Gross Profit and Gross Profit Margin (GPM) and explain their significance.
- Dive into a KNIME data app, where we visualize GPM for the entire year and break it down monthly.
Overview
ABC Furniture manufactures affordable furniture for lower/middle-class consumers and has a wide customizable range of products in its catalog. There are two main types of costs (COGS) for ABC:
- Production costs
- Warehousing costs
Production cost includes expenses for materials, such as wood and other necessary components, required to manufacture each piece of furniture. Warehousing costs cover the expenses for storing and distributing the furniture until it is sold. This includes storage fees, as well as the cost of managing and dispatching products to customers.
ABC Furniture has partnered with DEF Inc., a company that specializes in comprehensive warehousing services, to handle the storage of its products and manage deliveries to end customers
Given ABC Furniture’s varying production schedules, DEF Inc. provides a monthly breakdown of storage costs for each product. DEF Inc. has an efficient order fulfillment system which guarantees that orders are dispatched the very next day after the order is placed.
Considering all these costs, as the financial analyst at ABC Furniture, I will show you how to analyze both yearly and monthly Gross Profit Margin (GPM) in KNIME Analytics Platform.
Dataset
There are 5 CSV files used to monitor revenues and costs for ABC Furniture, via the workflow shown in Fig. 1. Both Revenue and Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) are computed in this workflow, and, subsequently, the GPM.
- invoices.csv - Orders received and their order value along with shipping charges, charged to the end customer.
- order_misc.csv - Relevant order details like storage entry date, order dispatch date, and delivery cost in delivering the order to the doorstep incurred by DEF Inc.
- prices.csv - Selling price for each product in the catalog.
- costs.csv - Breakdown of costs in manufacturing one piece of the product.
- inventory_storage_cost.csv - Storage cost for each product for the given month and year.
- products.csv - Product details such as product name and category (this file is not used in the workflow, but can be used to create additional views in the data app.).
Note. The objective of this article is to present how GPM can be analyzed in KNIME. Therefore, the dataset used for this example was artificially generated.
Using this data in our analysis, we will now learn about Gross Profit Margin (GPM). This key financial metric will help us assess the profitability of ABC Furniture by comparing revenue to the costs associated with producing and selling its products.
What is Gross Profit Margin (GPM)?
Gross Profit Margin (GPM) is a financial metric that measures the percentage of revenue left after deducting the costs associated with producing and storing goods or services. It reflects how well a company manages its production and sales by calculating the remaining revenue after accounting for the Costs of Goods Sold (COGS).
A higher GPM value indicates that the company is effectively managing its costs and has a competitive advantage in pricing. In contrast, a lower GPM value may indicate challenges in managing production or failure to strategize a better price point.
To elaborate on the calculation, Gross Profit (GP) is calculated by subtracting the the COGS from the revenue. Then GPM is calculated by expressing GP as a percentage of Revenue. It is important to note that GPM represents this percentage and not theGP itself (see formula below).
Once the gross profit is calculated, the GPM is calculated as follows.
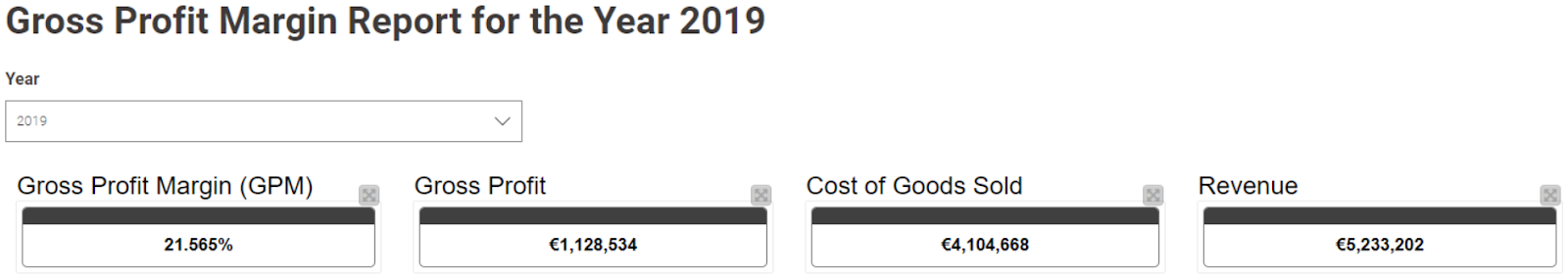
For example, in the dataset, revenue recorded for the year 2019 was €5,233,202 and the COGS was €4,104,668. Therefore as per the aforementioned formulation, the GP is calculated as follows:
Subsequently, the Gross Profit Margin is calculated as:
This means that 21.57% of the revenue in 2019 represents the profit allocated for overhead expenses and income tax of the company.
The calculations described above are performed within a KNIME workflow and the final output is visualized on a Data App in the form of scorecards (as seen in Fig 2). More details about the complete Data App will be provided in the “Visualization” section of this article.
What is Cost of Goods Sold and Revenue?
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the direct expenses associated with the production of goods that a company sells, including materials and labor costs. It represents the total cost of manufacturing products and is crucial for calculating gross profit and gross profit margin.
Revenue is the total income generated from the sale of goods or services before any expenses are deducted. It is an important measure of a company’s financial performance and serves as the starting point for assessing profitability.
In this use case, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) is calculated by summing up the delivery cost (the amount charged to ABC Furniture by DEF Inc.), storage cost, materials cost, assembly cost, and miscellaneous cost. The cost of producing any product is denoted as follows:
The final formula for calculating the COGS for each order is as follows:
It's important to note that this delivery cost is different from the shipping charges. Delivery cost is essentially the Outbound Delivery Cost which refers to the cost to deliver the furnished goods to the end customer. This is the cost endured by DEF Inc. in fulfilling the delivery. Whereas shipping charges are the cost added to the invoice by ABC Furniture.
This cost is higher than the delivery cost since ABC Furniture also profits from the shipping charges added to the invoice. Since ABC Furniture earns extra on shipping charges, this cost is added to Revenue, and delivery costis added to the COGS.
Visualization
In this section, we will explore the results and visualizations produced by a data app in KNIME. It will help us understand how Gross Profit Margin (GPM) can be effectively displayed for both annual and monthly analyses.
This example shows a straightforward solution in KNIME Analytics Platform to visualize GPM for the year as a whole and also for the monthly breakdown. The computed fields of Revenue, COGS, GP, and GPM are aggregated across all months for the selected year and are visualized in Fig. 3. In the visualization, you can see the scorecards at both, the top and bottom showing the monthly breakdown. For simplicity, the Data App only uses TileView and BarChart visualization nodes, however, these are not the only options available for creating interactive dashboards in KNIME. For more information on the supported chart types, refer here.
Figure 3 shows that the gross profit margin (GPM) for the selected year ranges around 30%. Even the monthly breakdown for 2018, has the same results. This indicates that the company is maintaining a stable profitability but isn’t showing signs of growth or improvement in its production efficiency. In the long term, this is not sustainable for the business as increased market competition could make it difficult for the company to remain competitive.
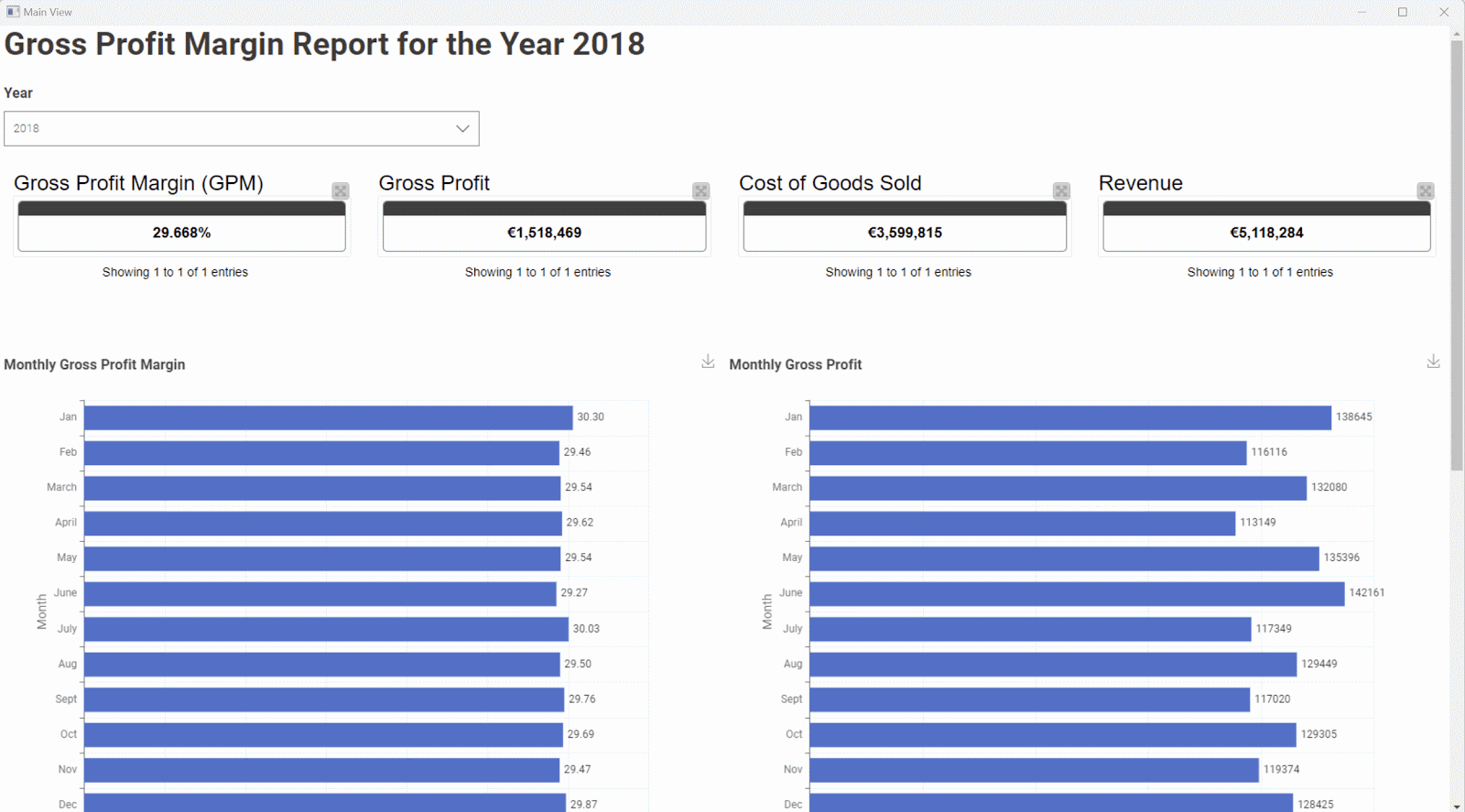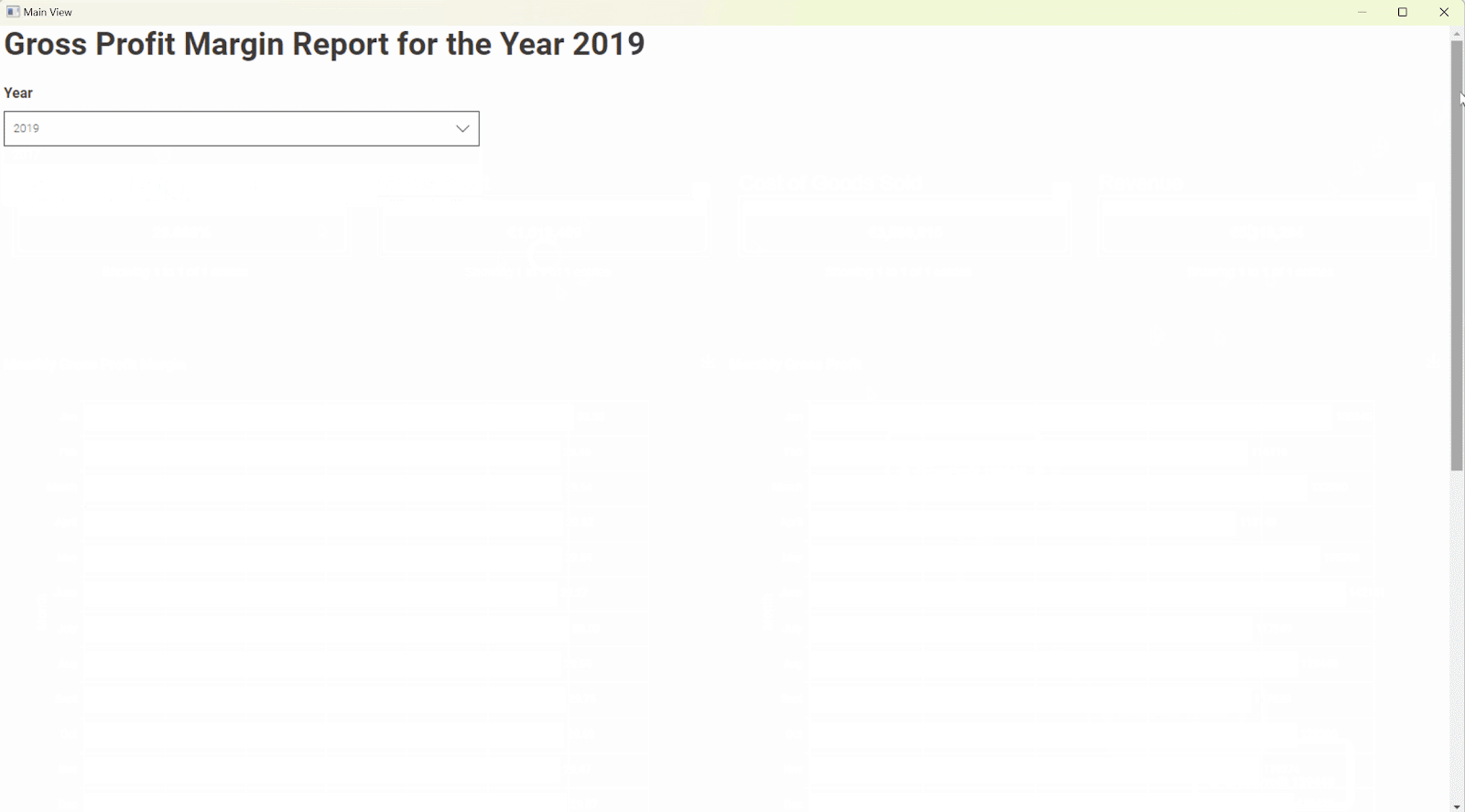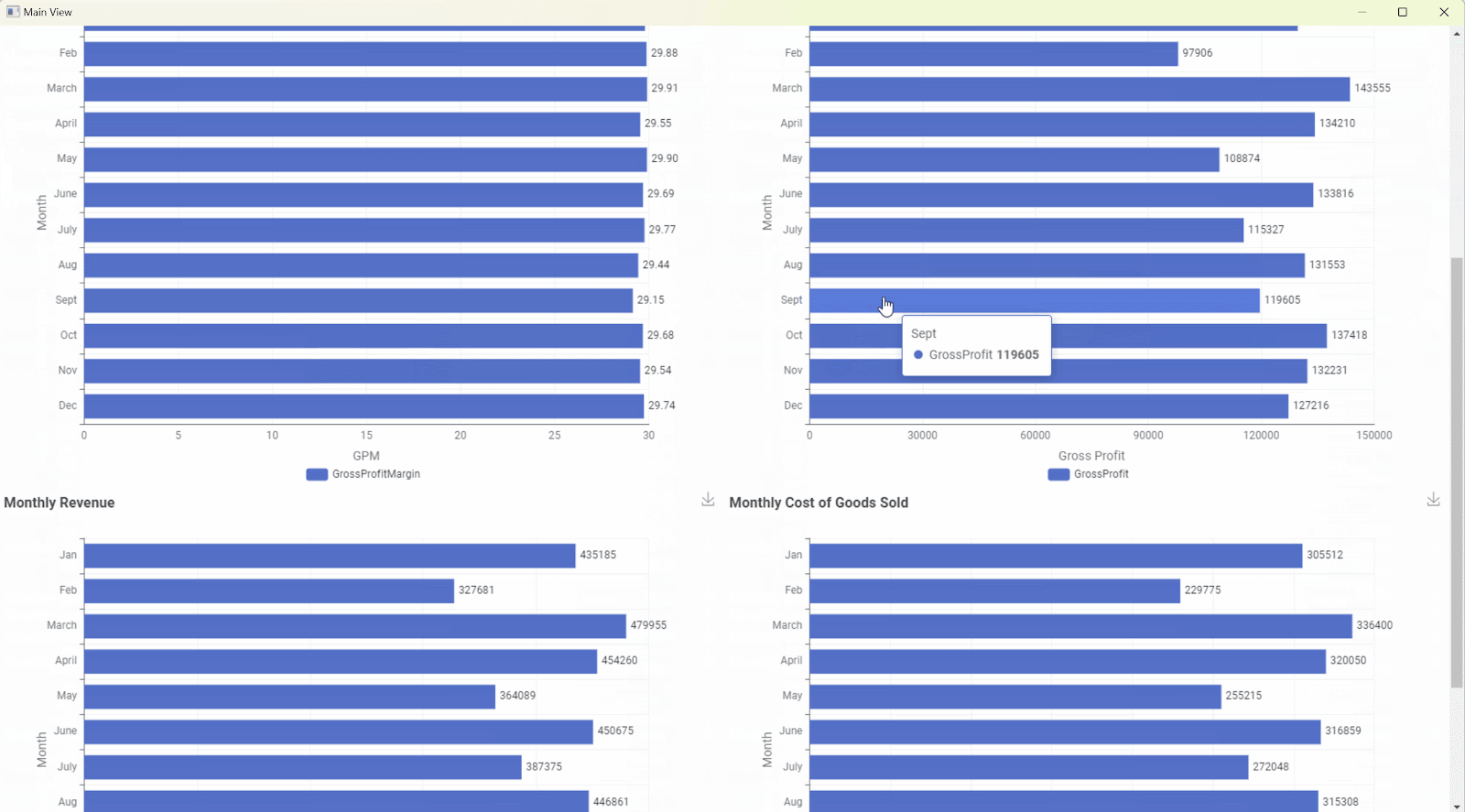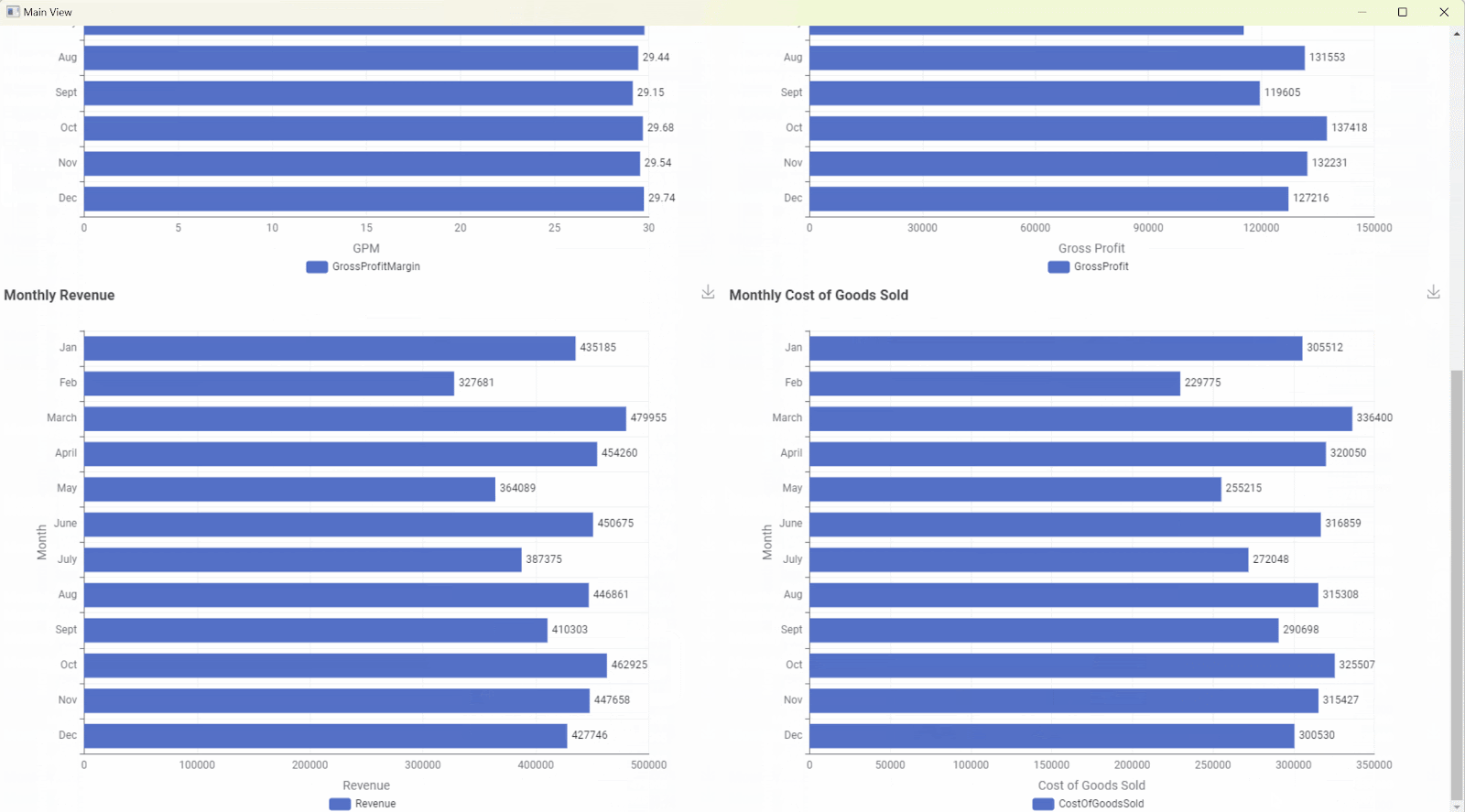 Fig. 3: Final view of the data app.
Fig. 3: Final view of the data app.In this article, we covered the analysis of Gross Profit Margin (GPM) for the ABC Furniture company using data from multiple CSV files that are read into a KNIME workflow. After transforming the data and applying the GP and GPM formulas discussed earlier, we created an interactive Data App in KNIME to visualize both yearly and monthly GPM along with its respective components for the selected year. The Data App consists of scorecards that give an overall picture of the performance and a set of bar charts that visualize the monthly breakdown.
Additionally, this Data App can be further detailed by adding more views to visualize the breakdown of revenue and COGS, based on sold products, or product categories so that only the top ten or top five products or categories are displayed in a view.
To learn more about analyzing different financial metrics in KNIME, you can explore the KNIME for Finance collection on the KNIME Community Hub.
